-
Technical Note
-
암반 양수시험-회복자료 분석 방안 검토
Evaluation of Analysis Approaches for Recovery Data Following Pumping Tests in Fractured Rock
-
이항복, 박정욱, 박의섭, 박찬
Hangbok Lee, Jung-Wook Park, Eui-Seob Park, Chan Park
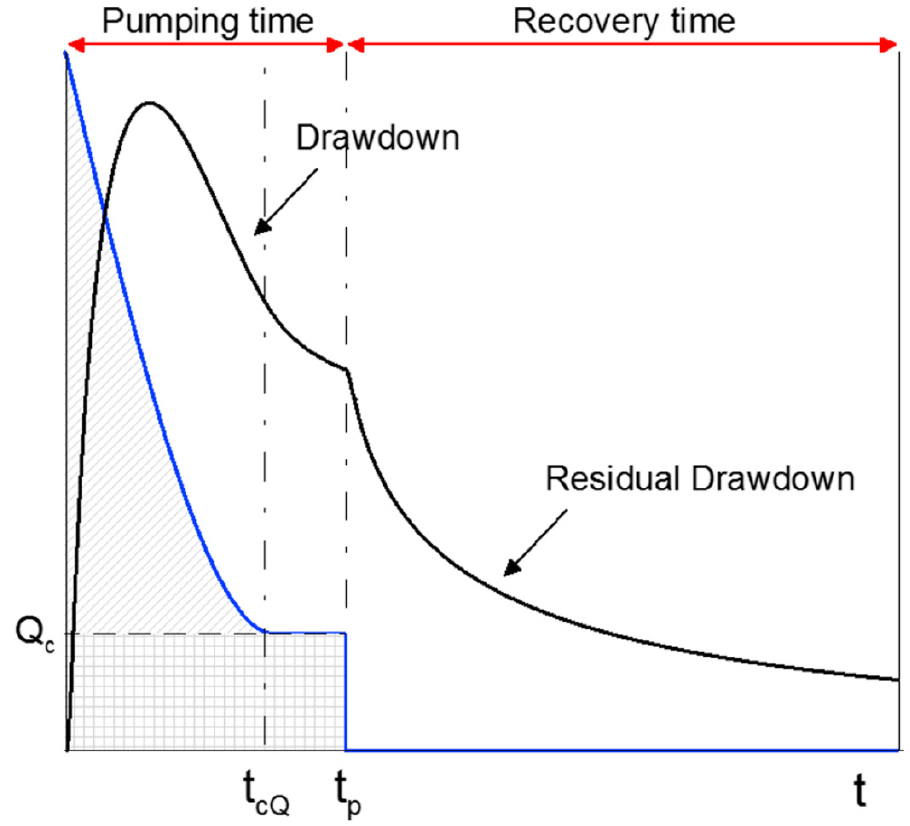
- 본 보고에서는 암반 내에서 수행된 양수시험 이후 회복자료를 분석하기 위한 회복해석 기법에 대해 검토하였다. 암반대수층 특성화를 위한 양수시험은 진단 플롯을 활용하여 암반 …
This report reviews key recovery analysis methods for interpreting drawdown recovery data following pumping tests conducted in fractured bedrock. Pumping tests are …
- 본 보고에서는 암반 내에서 수행된 양수시험 이후 회복자료를 분석하기 위한 회복해석 기법에 대해 검토하였다. 암반대수층 특성화를 위한 양수시험은 진단 플롯을 활용하여 암반 지하수계에 대한 개념적 이해를 도모하고, 수리상수를 추정하기 위한 목적으로 수행한다. 회복시험은 양수 종료 후, 양수공 및 관측공에서의 수위회복 반응을 측정하는 방식으로 이루어지며, 특히 정확한 양수 유량 제어가 어려운 현장 상황에서 유용하게 활용될 수 있다. 전통적으로 회복시험은 Theis 회복해석법을 기반으로 발전해왔으며, 이를 바탕으로 다양한 해석 기법들이 도입되어 왔다. 이들 분석법은 유효 투수도에 대한 신뢰성 있는 추정을 가능하게 하지만, 암반대수층의 개념적 수리 유동 모델에 대한 구체적인 정보는 제공하지 못하는 한계가 존재한다. Agarwal은 회복 데이터를 기반으로 초기 및 후기 수리반응을 모두 반영하는 해석 기법을 제안했으며, 현재는 암반수리지질 및 석유 산업 분야에서 표준 해석 분석법으로 널리 활용되고 있다. 이 분석법은 회복곡선을 일정 유량 조건 하의 등가 양수곡선으로 변환하여 재현함으로써, 우수한 수리상수 추정 결과를 제공할 뿐만 아니라, 개념적 유동 모델의 설정과 해석에도 효과적으로 기여할 수 있다. 본 보고에서는 Agarwal 분석법을 적용한 양수-회복시험 사례를 검토하여, 복잡하고 비이상적인 유동 조건 하에서 수집된 제한적이고 불확실성을 내포한 수리시험 자료의 해석 가능성과 활용성을 평가하였다. 이를 통해, 암반의 수리특성 평가 정확도를 향상시키기 위한 해석 기법으로서의 Agarwal 분석법의 적용 가능성을 검토하고자 한다.
- COLLAPSE
This report reviews key recovery analysis methods for interpreting drawdown recovery data following pumping tests conducted in fractured bedrock. Pumping tests are widely used for characterizing fractured aquifers, employing diagnostic plots to enhance the conceptual understanding of groundwater flow systems and to estimate hydraulic parameters. Recovery testing involves measuring the water level rebound in pumping and observation wells after the termination of pumping and is particularly useful under field conditions where precise control of discharge rates is difficult. Traditionally, recovery data have been analyzed based on the Theis recovery method, which has provided the foundation for various extended analytical approaches. While these methods offer reliable estimates of effective transmissivity, they are limited in providing specific insights into the conceptual flow models of fractured aquifers. Agarwal introduced an analysis technique capable of incorporating both early and late time hydraulic responses using recovery data. This method has since become a standard approach in both hydrogeological and petroleum reservoir engineering fields. The Agarwal method transforms recovery curves into equivalent drawdown curves under constant-rate pumping, thereby enhancing the accuracy of parameter estimation and contributing to the identification of appropriate conceptual flow models. This report examines case studies where the Agarwal method was applied to pumping-recovery test data, evaluating its applicability for interpreting limited and uncertain test results under complex, non-ideal flow conditions. The findings suggest that the Agarwal approach holds significant potential as an effective analytical tool for improving the accuracy of hydraulic characterization in fractured rock environments.
-
암반 양수시험-회복자료 분석 방안 검토
-
Original Article
-
완충재가 충전된 암석 절리면의 전단 크리프 거동 특성에 관한 실험적 연구
Experimental Study on Shear Creep Behavior of Rock Joint Surfaces Filled with Buffer Material
-
김현식, 최승범, 하성준, 정호영
Hyun-Sik Kim, Seungbeom Choi, Sung-Jun Ha, Hoyoung Jeong
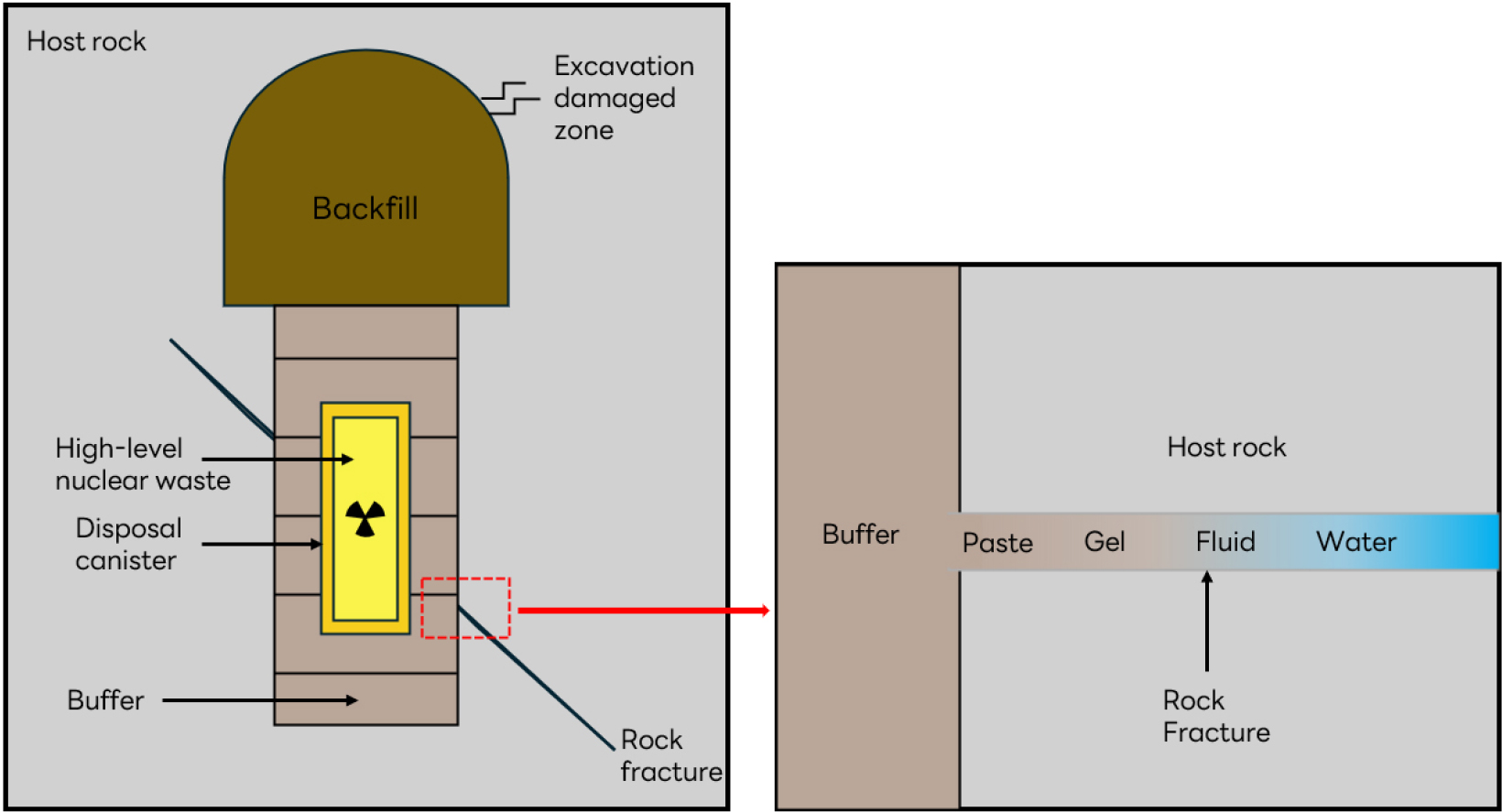
- 본 연구는 심층처분 환경에서 절리면을 따라 침투한 완충재가 암반 불연속면의 장기 안정성에 미치는 영향을 평가하기 위해 수행되었다. 국내 황등화강암 절리면을 대상으로 완충재를 …
This study evaluates the influence of buffer material infiltration on the long-term stability of rock discontinuities in deep geological disposal environments. Shear …
- 본 연구는 심층처분 환경에서 절리면을 따라 침투한 완충재가 암반 불연속면의 장기 안정성에 미치는 영향을 평가하기 위해 수행되었다. 국내 황등화강암 절리면을 대상으로 완충재를 도포한 후 전단 크리프 시험을 수행하였으며, 완충재 충전에 따른 절리면 거칠기 변화와 크리프 거동을 분석하였다. 시험은 수직응력 3.0 MPa로 수행하였으며, 전단응력은 최대전단강도 대비 94%~75%로 단계적으로 응력을 변화시켜가며 진행하였다. 시험 전·후 휴대용 3D 스캐너로 절리면을 스캔하여 거칠기 및 최대전단강도를 산정하였다. 그 결과, 완충재가 불연속면 사이에 충전된 경우, 거칠기 감소가 국부적으로 진행되는 경향을 보였으며, 94%~75% 전단응력 수준에서 4일간 관측된 전단 변형은 3차 크리프로 전이되지 않았다. 여러 크리프 모델의 적합성을 평가한 결과, Burger 모델은 전반적으로 실험 데이터를 나타내기에 적합하였으나 물리적으로 적합하지 않은 크리프 상수를 도출하는 경향이 있었다. 반면, Nishihara 모델은 Burger 모델 대비 높은 적합성을 나타내었다. 다만, 본 연구에서 도출된 크리프 상수는 제한된 시험조건에서 완충재 두께 및 응력 수준에 대해 일관된 경향성을 보이지 않았으며, 향후 다양한 절리면 조건, 완충재 두께, 응력 수준을 고려한 추가 실험을 통해 크리프 거동의 정밀 분석이 필요할 것으로 판단되었다.
- COLLAPSE
This study evaluates the influence of buffer material infiltration on the long-term stability of rock discontinuities in deep geological disposal environments. Shear creep tests were performed on Hwangdeung granite joints infilled with buffer material under a normal stress of 3.0 MPa. Shear stress levels were applied stepwise from 75% to 94% of the peak shear strength, and joint roughness was analyzed using 3D scanning before and after testing. Results indicated that buffer infilling led to localized reductions in joint roughness, and no transition to tertiary creep was observed during the 4-day observation period. In the suitability analysis of various creep models, the Nishihara model demonstrated higher fitting accuracy than the Burger model, which yielded physically inconsistent creep constants. Due to the inconsistent trends of constants regarding buffer thickness and stress levels, further experimental research under diverse conditions is necessary for a precise analysis of creep behavior.
-
완충재가 충전된 암석 절리면의 전단 크리프 거동 특성에 관한 실험적 연구
-
Original Article
-
저심도 연약 퇴적 암반 터널의 스폴링 및 지보재 손상 메커니즘 규명
Evaluation of Spalling and Support Damage Mechanism of a Tunnel in Weak Sedimentary Rock Mass at Relatively Shallow Depth
-
이희석, 이재욱, 홍의준, 전태식, 문연오, 고상준
Hee Suk Lee, Jaewook Lee, Eui Joon Hong, Tae Sik Jeon, Yeon Oh Moon, Sang Joon Ko
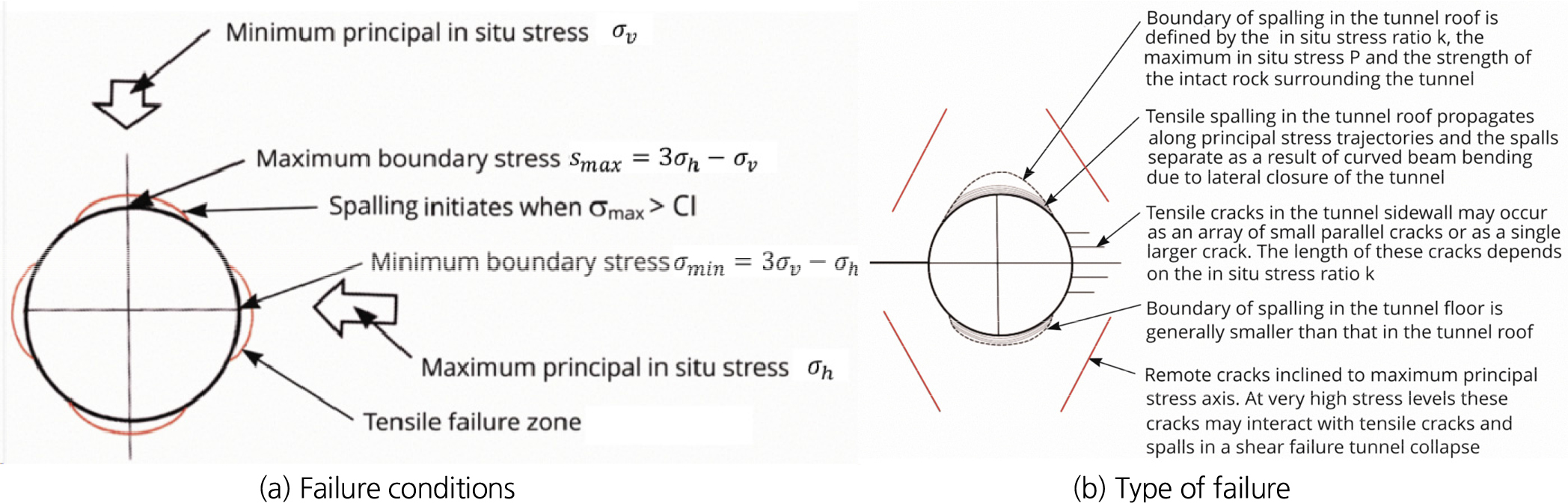
- 취성파괴 또는 스폴링 현상은 일반적으로 심부 고강도 결정질 암반에서 발생하는 현상으로 알려져 있다. 본 연구는 약 90 m의 비교적 얕은 심도, 저강도(약 …
Brittle failure and spalling are typically associated with high-strength crystalline rocks at great depths. However, this study investigates an exceptional case of …
- 취성파괴 또는 스폴링 현상은 일반적으로 심부 고강도 결정질 암반에서 발생하는 현상으로 알려져 있다. 본 연구는 약 90 m의 비교적 얕은 심도, 저강도(약 30 MPa) 퇴적 암반에 굴착된 터널에서 발생한 이례적인 스폴링 및 지보재 손상 사례를 조사하였다. 해당 현장에서는 숏크리트 균열과 록볼트의 파단을 포함한 과도한 변위가 관찰되었다. 현장 조사와 시추공 내시경 분석 결과, 이러한 손상은 지형적 특성으로 인한 이상 응력 조건과 암석의 취성적 특성이 결합하여 발생한 것으로 확인되었다. 특히 층리 등의 지질구조는 스폴링과 슬래빙 메커니즘을 결합시켜 손상을 가속화 하는 것으로 나타났다. 이론 및 수치해석 결과, 기존 심부 결정질 암반에서 정립된 “응력-스폴링 깊이” 관계가 본 사례와 같은 천부 퇴적암에도 적용 가능함을 입증하였다. 본 연구는 이례적인 응력 환경에서 연암의 취성 거동이 터널 지보 설계에 미치는 영향을 규명하였다는 점에서 의의가 있다.
- COLLAPSE
Brittle failure and spalling are typically associated with high-strength crystalline rocks at great depths. However, this study investigates an exceptional case of spalling and support failure in a weak sedimentary rock mass at a shallow depth of 90 m. Despite a low compressive strength (~30 MPa), excessive displacements, shotcrete cracking, and rock bolt ruptures were observed. Field evaluations and borehole endoscopy confirmed that the damage resulted from spalling, triggered by brittle rock characteristics and anomalous stress conditions from specific topographical features. The study also found that bedding planes can exacerbate this by combining spalling with slabbing mechanisms. Numerical analyses validated that the stress-spalling depth relationship established for deep crystalline rocks remains applicable here. These findings highlight the necessity of considering brittle behavior in weak rocks to optimize tunnel support design in unconventional stress environments.
-
저심도 연약 퇴적 암반 터널의 스폴링 및 지보재 손상 메커니즘 규명
-
Original Article
-
고준위방사성폐기물 심층처분을 위한 국내 심부 화강암 열물성 특성 평가
Measurement and Analysis of Thermal Properties of Deep Granite in Korea for HLW Geological Disposal
-
천대성, 이재원, 이상빈, 김형찬, 최준형, 김기석, 정종원
Dae-Sung Cheon, Jaewon Lee, Sangbeen Lee, Hyungchan Kim, Junhyung Choi, Ki Seog Kim, Jongwon Jung
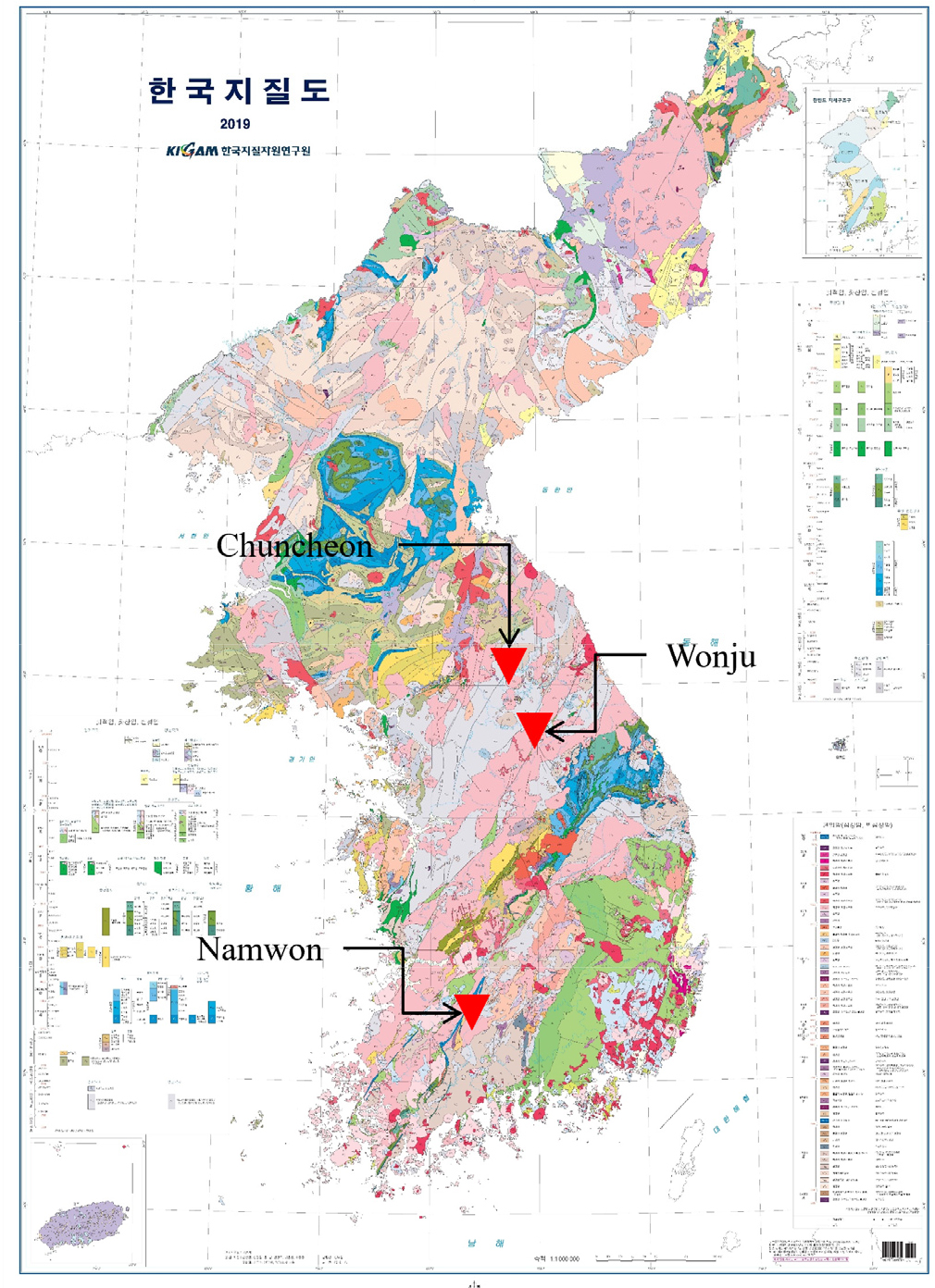
- 현재 국내에서는 원자력 발전의 부산물인 고준위방사성폐기물 저장용량의 79.6%가 포화했으며 일부 원전은 2030년대에 포화가 예상된다. 고준위방사성폐기물은 장기간 열과 방사선을 방출하기 때문에 지하 500 …
In South Korea, 79.6% of the storage capacity for High-radioactive waste (HLW) has been reached, with some nuclear power plants expected to …
- 현재 국내에서는 원자력 발전의 부산물인 고준위방사성폐기물 저장용량의 79.6%가 포화했으며 일부 원전은 2030년대에 포화가 예상된다. 고준위방사성폐기물은 장기간 열과 방사선을 방출하기 때문에 지하 500 m 내외의 암반층에 처분하는 심층 처분이 고려되고 있다. 따라서 부지 선정 과정에서 암반의 열물성을 고려할 필요가 있다. 하지만 국내에서는 심부 암반에 대해 열물성을 측정한 사례가 부족하다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 화강암반에 있는 남원, 원주, 춘천에서 750 m까지 시추하여 확보한 암석을 TPS, LFA로 열물성을 측정하였다. 심도에 따른 열전도도 경향은 없었으며 열전도도와 열확산율 사이 비례 관계를 확인하였다. 그리고 XRD 분석을 통해 조암광물 함량비가 암석의 열전도도에 영향을 미치는 주요한 인자로 나타났다. 본 연구 결과는 향후 심층처분장 부지 선정 시 기초 자료로 활용될 것으로 기대된다.
- COLLAPSE
In South Korea, 79.6% of the storage capacity for High-radioactive waste (HLW) has been reached, with some nuclear power plants expected to face full saturation by the 2030s. Since HLW continuously emits heat and radiation over extended periods, deep disposal at depths of approximately 500 m is being considered as a viable solution. Consequently, it is essential to evaluate the thermal properties of the rock mass during the site selection process. However, there is a lack of measured data regarding the thermal properties of deep rock masses in South Korea. In this study, rock samples were obtained from boreholes drilled to depths of up to 750 m Namwon, Wonju, and Chuncheon, and their thermal properties were measured using Transient plane source method (TPS) and Laser flash method (LFA). The results indicated no significant trend in thermal conductivity with respect to depth; however, a proportional relationship between thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity was confirmed. Furthermore, X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis revealed that the mineral composition is a primary factor influencing the thermal conductivity of the rocks. These findings are expected to serve as foundational data for the future selection of deep disposal sites.
-
고준위방사성폐기물 심층처분을 위한 국내 심부 화강암 열물성 특성 평가
-
Original Article
-
열적 효과가 함열 화강암 절리의 전단-수리 거동에 미치는 영향에 관한 실험적 연구
Experimental Study on the Thermal Effect on the Shear-Flow Behaviors of Hamyeol Granite Joints
-
하성준, 김태현, 김진섭
Seong Jun Ha, Taehyun Kim, Jin-Seop Kim
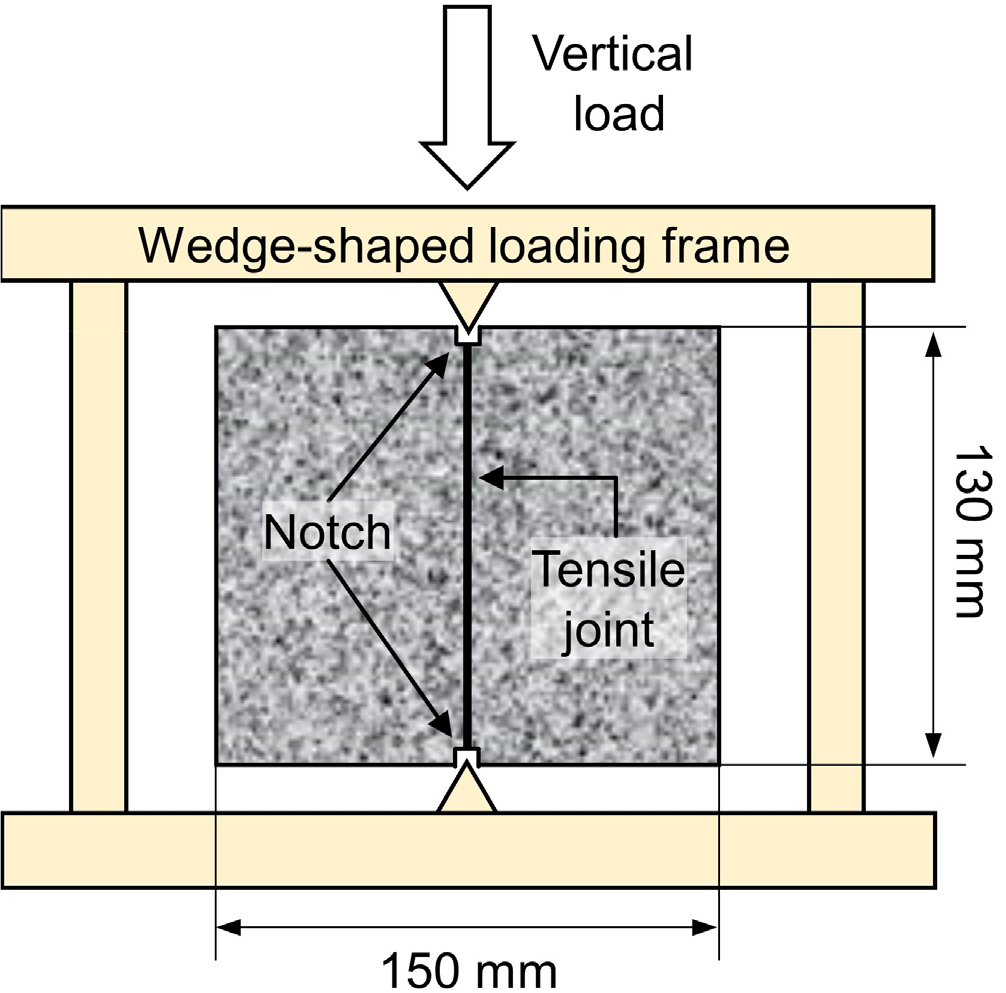
- 심부 암반은 다수의 절리를 포함하는 복합 구조체로, 이러한 불연속면은 역학적 취약부이자 지하수 유동의 주요 경로로 작용하므로 열-수리-역학적 복합 거동 규명이 필수적이다. 특히 …
Deep rock masses are complex structures characterized by numerous joints. These discontinuities serve as mechanical weaknesses and primary pathways for groundwater flow, …
- 심부 암반은 다수의 절리를 포함하는 복합 구조체로, 이러한 불연속면은 역학적 취약부이자 지하수 유동의 주요 경로로 작용하므로 열-수리-역학적 복합 거동 규명이 필수적이다. 특히 전단 하중과 온도 변화가 결합될 경우, 암석 매질의 열팽창과 전단 팽창이 수리적 특성에 미치는 영향은 매우 복잡한 양상을 띤다. 본 연구에서는 화강암 절리의 전단-수리 거동에 열적 효과가 미치는 영향을 조사하기 위해 상온 및 고온 조건에서 전단-수리 복합 실험을 수행하였다. 실험 과정은 전단 전, 전단 중, 잔류의 세 단계로 구분되었으며, 각 단계에서 절리에 대한 수직 응력 및 주입압 변화에 따른 투수 특성을 정밀하게 계측하였다. 연구 결과, 전단 전 단계에서는 수직 응력 증가와 열팽창에 의한 열적 닫힘 효과로 투수성이 감소하였으나, 전단 파괴 시 발생하는 전단 팽창이 이를 압도하여 유량이 초기 대비 100배 이상 급증하였다. 특히 잔류 단계에서는 전단 팽창 효과가 지배적으로 작용하여 온도 조건에 관계없이 수리적 거동이 유사해지는 양상을 보였다.
- COLLAPSE
Deep rock masses are complex structures characterized by numerous joints. These discontinuities serve as mechanical weaknesses and primary pathways for groundwater flow, making it essential to characterize their coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical behavior. In this study, shear-flow coupled tests were conducted on granite joints at both ambient and elevated temperatures to investigate the influence of thermal effects on shear-flow behavior. The experimental procedure was categorized into three distinct stages: pre-shear, during-shear, and residual. During each stage, permeability characteristics were precisely measured in response to changes in joint normal stress and injection pressure. In the pre-shear stage, permeability decreased due to the thermal closure effect caused by thermal expansion and increased normal stress. However, during shear failure, the flow rate surged by more than 100 times compared to the initial state, as the effect of shear dilation significantly overwhelmed thermal expansion. In the residual stage, shear dilation remained the dominant factor, leading to convergent flow behaviors regardless of the temperature conditions.
-
열적 효과가 함열 화강암 절리의 전단-수리 거동에 미치는 영향에 관한 실험적 연구



 Tunnel and Underground Space
Tunnel and Underground Space











