-
Technical Note
-
고준위방사성폐기물 처분부지연구를 위한 심부 시추공 공곡 측정 및 공곡도 향상 방안
Measurement and Mitigation Strategies of Borehole Deviation in Deep Drilling for High-Level Radioactive Waste Disposal Site Study
-
천대성, 박재용, 이성곤, 김기석
Dae-Sung Cheon, Jai-Yong Park, Seong Kon Lee, Ki Seog Kim
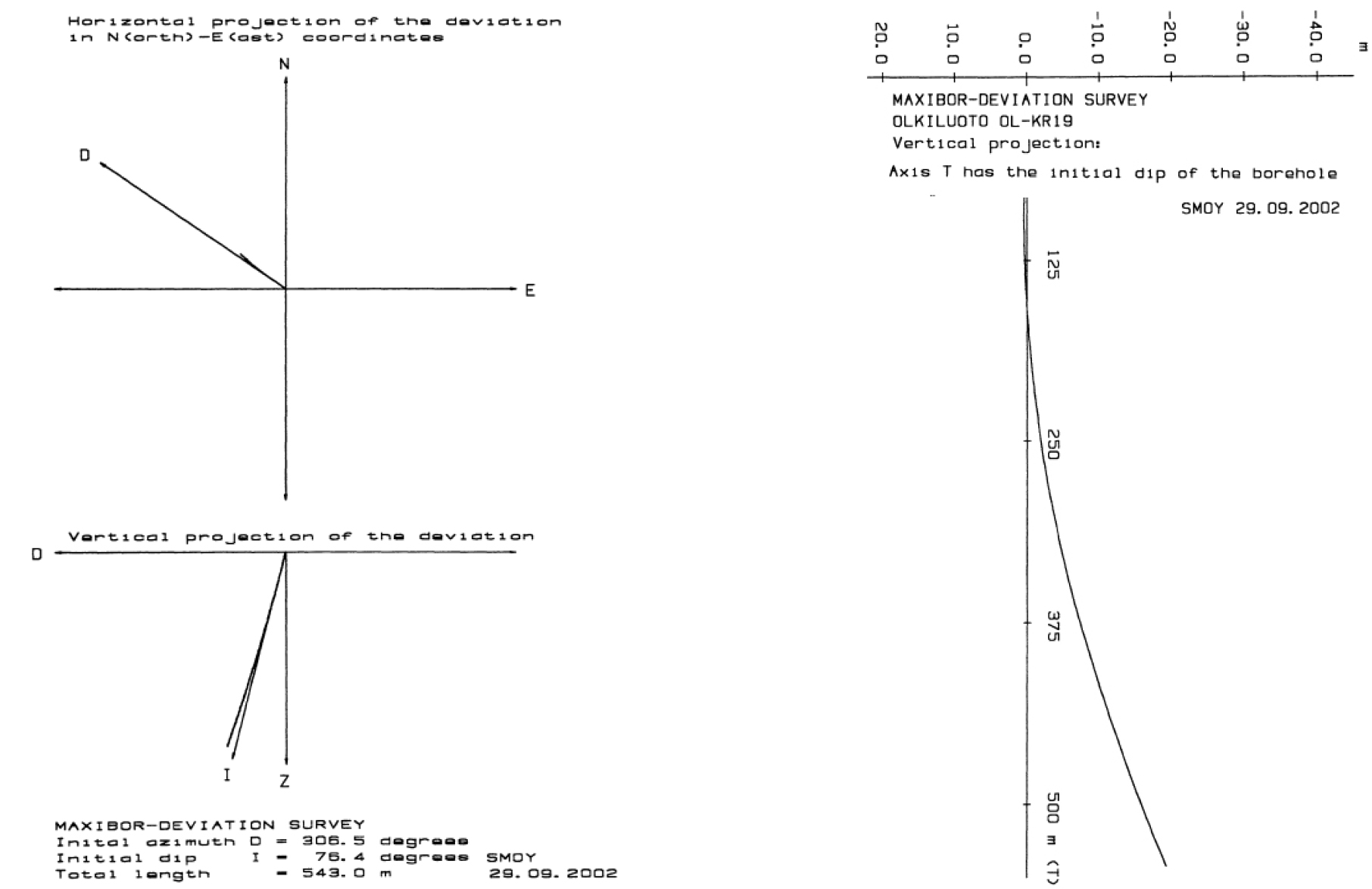
- 공곡은 수직, 수평, 경사 등을 포함하는 시추 방향 기준으로 실제 굴진할 때 시추공의 휜 정도를 뜻하며, 고준위방사성폐기물 심층 처분시설 설계의 정확도에 영향을 …
Borehole deviation refers to the degree of curvature that occurs during actual drilling relative to the intended drilling direction. Since borehole deviation …
- 공곡은 수직, 수평, 경사 등을 포함하는 시추 방향 기준으로 실제 굴진할 때 시추공의 휜 정도를 뜻하며, 고준위방사성폐기물 심층 처분시설 설계의 정확도에 영향을 주기 때문에 정밀한 측정과 적절한 공곡 관리가 요구된다. 본 보고에서는 국내·외 공곡 측정에서 활용되는 장비의 종류와 원리를 소개하고, 핀란드와 스웨덴의 공곡 측정 사례와 공곡 발생 원인, 공곡의 재산정 등에 대해 소개하였다. 또한 국내에서 고준위방사성폐기물 처분장의 부지연구에서 수행되었던 약 750 m 심도의 암종별 시추공에서 획득한 공곡 결과를 제시하였다. 대부분 심부 시추공에서 1° 전후의 공곡이 발생하였으며, 층리와 엽리, 편리 등이 있는 암종에서 공곡이 상대적으로 약간 크게 발생하는 것을 알 수 있었다. 그러나 시추장비가 위치한 지반 상태가 열악하고, 시추 중 다수의 연약대와 만났던 편마암반의 시추공에서는 7°를 넘는 공곡이 발생하였고, 공곡 초과 발생 원인은 시추장비가 위치한 지반 내 존재했던 큰 규모의 전석들과 시추 과정에서 자주 나타난 연약대와 파쇄대 등에 의해 영향을 받은 것으로 파악되었다. 국내 심부 시추 경험과 국외 사례 조사에 기반하여 심부 시추공의 공곡 완화 및 향상 방안으로 다단식 시추와 보호 케이싱 설치, 시추장비 위치의 콘크리트 패드 설치, 시추 시작 또는 시추 중 시추장비에 대한 수평, 수직계를 이용한 측정 및 관리, 적절한 시추 속도 유지, 시추 중 드릴칼라나 스테빌라이져의 이용 등을 제시하였다.
- COLLAPSE
Borehole deviation refers to the degree of curvature that occurs during actual drilling relative to the intended drilling direction. Since borehole deviation affects the accuracy of deep geological repository design for high-level radioactive waste, precise measurement and proper management are required. This article introduces the types and principles of instruments used for borehole deviation measurement both domestically and internationally, presents case studies from Finland and Sweden, and discusses the causes of borehole deviation and methods for its reassessment. In addition, borehole deviation results obtained from boreholes drilled at depths of approximately 750 m in various rock types during site study for a domestic high-level radioactive waste repository are presented. Most deep boreholes exhibited deviations of around 1°, with relatively larger deviations observed in rock types with stratification, foliation, or schistosity. However, in gneissic rock boreholes where drilling equipment was set on poor ground conditions and multiple weak zones were encountered during drilling, deviations exceeding 7° occurred. The excessive deviation was attributed to the influence of large boulders in the ground where drilling equipment was installed and to frequent weak and fractured zones encountered during drilling. Based on domestic deep drilling experience and international case studies, potential strategies for mitigating and improving borehole deviation include multi-stage drilling, installation of protective casing, placement of concrete pads for drill rig positioning, use of horizontal and vertical measurement devices for drill rig alignment at the start or during drilling, maintaining appropriate drilling rates, and employing drill collars or stabilizers during drilling.
-
고준위방사성폐기물 처분부지연구를 위한 심부 시추공 공곡 측정 및 공곡도 향상 방안
-
Technical Note
-
유압시스템의 물리적 거동해석을 위한 다물체 동역학-유압 연동모델 시뮬레이션
Co-Simulation of Multibody Dynamics and Hydraulic Systems for Physical Behavior Analysis
-
이홍석
Hong-Seok Lee
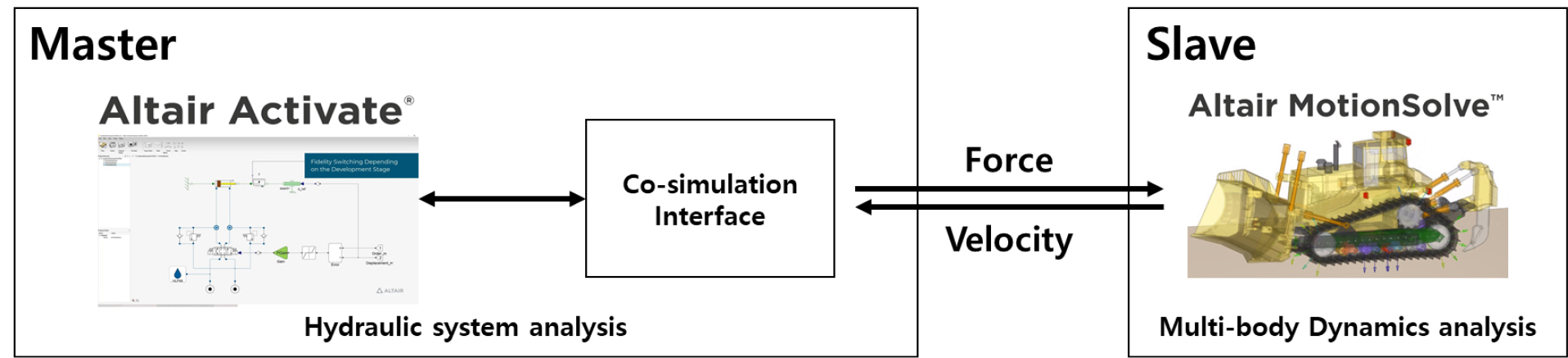
- 본 연구에서는 연속굴착형 TBM의 다물체 동역학 해석과 유압시스템 해석을 연동한 시뮬레이션 모델을 구축하였다. 이를 통해 추진잭의 추력 거동 분석과 제어 시스템 성능 …
A co-simulation model integrating the multibody dynamics of a continuous excavation-type tunnel boring machine (TBM) with its hydraulic system was constructed. The …
- 본 연구에서는 연속굴착형 TBM의 다물체 동역학 해석과 유압시스템 해석을 연동한 시뮬레이션 모델을 구축하였다. 이를 통해 추진잭의 추력 거동 분석과 제어 시스템 성능 평가를 가상환경에서 수행하고자 하였다. 일률 교환 피드백 구조를 가진 연동모델을 적용하여, 추진잭의 압력 변화가 동역학시스템에 반영되고, 이때 발생하는 속도를 유압시스템의 부하로 반영되도록 구성하였다. 이를 통해 추진잭의 하중 분포, 압력 응답, 및 추력 중심(Center of Thrust, COT) 제어 과정을 구현하였다. 또한, 기존의 일괄 제어형 유압 회로를 개선하여, 각 추진잭에 압력센서를 1:1로 대응시킨 독립 제어 구조를 모델링하였다. 헬리컬 세그먼트 경사면으로 인해 추진잭 간 접촉 거리 차이가 발생하며, 각 추진잭 간의 시간에 따른 압력 응답의 변화를 확인할 수 있었다. 또한, 설정된 COT 목표 각도에 따라 추진잭의 압력을 제어한 결과, COT 제어의 유효성이 검증되었다. 제안된 다물체-유압 연동 해석 모델은 실제 TBM 유압제어시스템 설계단계에서, 추진 모듈의 하중 분포, 유압 응답, 및 제어 알고리즘의 타당성을 사전에 검증할 수 있을 것으로 판단된다.
- COLLAPSE
A co-simulation model integrating the multibody dynamics of a continuous excavation-type tunnel boring machine (TBM) with its hydraulic system was constructed. The proposed model enables the evaluation of the thrust jack behavior and control system performance within a virtual simulation environment. The coupled model employs a power-exchange feedback structure, in which pressure variations in the thrust jacks are reflected in the dynamic system, and the resulting velocity responses are fed back as loads to the hydraulic system. Through this approach, the load distribution, pressure response, and Center of Thrust (COT) control behavior of the thrust system were realized. Furthermore, the conventional group-controlled hydraulic circuit was improved by introducing an independent control architecture, in which each thrust jack is individually equipped with a dedicated pressure sensor. Due to the inclined surface of the helical segments, differences in the contact distance among the thrust jacks were observed, resulting in corresponding variations in the time-dependent pressure responses. By controlling the jack pressures according to the specified COT target angles, the effectiveness of the proposed COT control method was verified. The implemented multibody–hydraulic co-simulation model can be effectively utilized in the design phase of TBM hydraulic and control systems to validate the load distribution, hydraulic response, and control algorithm of the thrust module in advance.
-
유압시스템의 물리적 거동해석을 위한 다물체 동역학-유압 연동모델 시뮬레이션
-
Case Study
-
글로벌 주요 제조사의 광산용 무인 적재 장비 기술 동향 및 국내 도입 사례
Technological Trends of Mining Unmanned Loading Equipment by Global Manufacturers and Implementation Cases in Korea
-
장민경, 최요순
Mingyeong Jang, Yosoon Choi
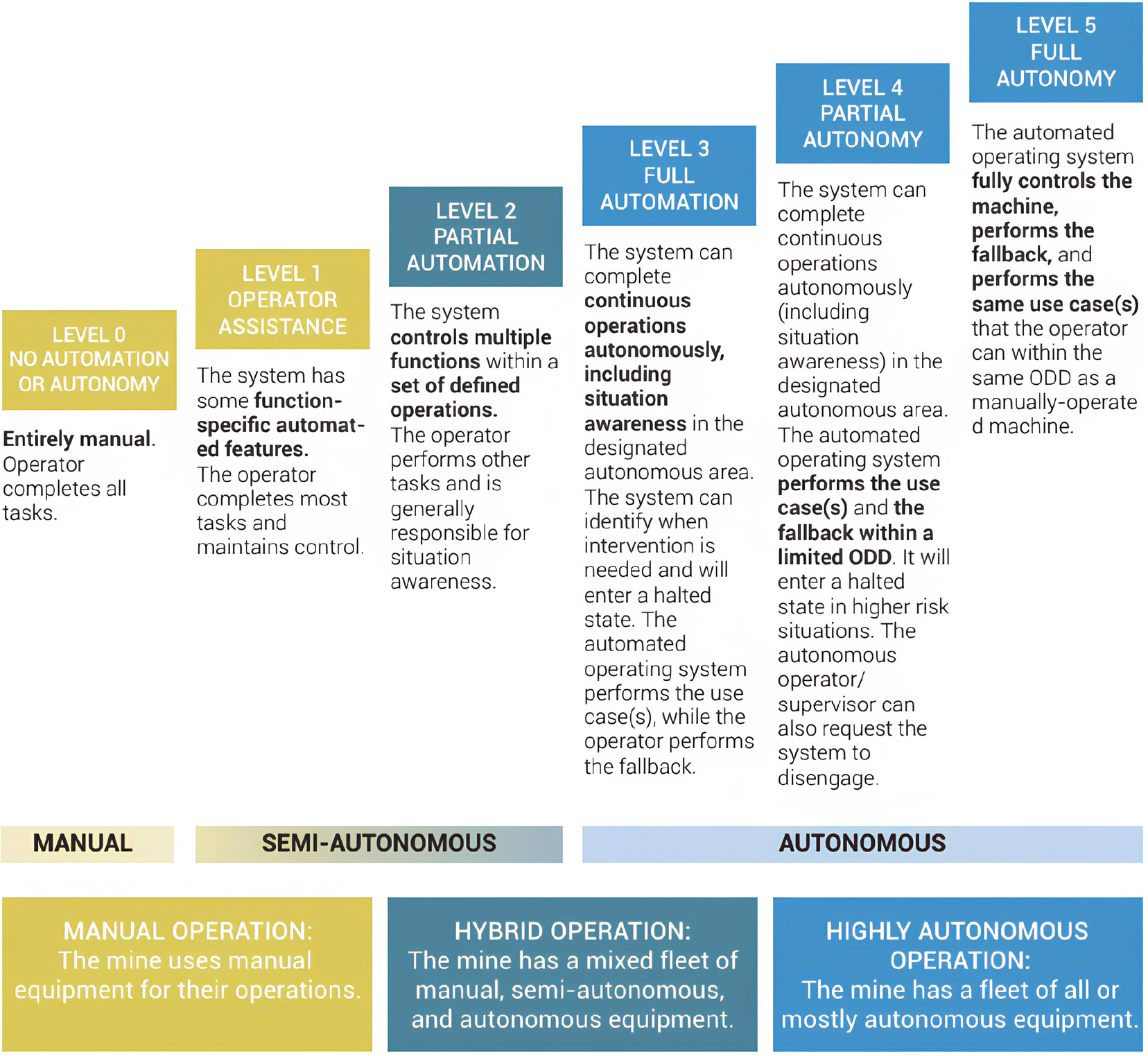
- 본 연구는 광산 무인화를 위한 자율적재시스템과 무인 적재 장비의 개념 및 기술 구조를 정립하고, 글로벌 주요 제조사의 개발 동향과 현장 적용 사례를 …
This study defines autonomous loading systems and unmanned loading equipment in mining and reviews development trends and applications by major global manufacturers. …
- 본 연구는 광산 무인화를 위한 자율적재시스템과 무인 적재 장비의 개념 및 기술 구조를 정립하고, 글로벌 주요 제조사의 개발 동향과 현장 적용 사례를 비교·분석하였다. 또한 GMG의 광산 자동화 성숙도 모델을 적용해 제조사별 시스템의 자동화 수준을 평가하였다. 분석 결과, 현재 무인 로더와 굴착기는 주로 원격 조종 기반으로 운용되며, LiDAR·카메라·GPS 센서 융합을 통한 실시간 위치 인식과 객체 탐지·장애물 회피·안전 기능, 그리고 Wi-Fi 등 무선 통신을 활용한 제어 및 데이터 송수신 체계를 공통적으로 포함한다. 자동화 성숙도는 대부분 Level 1–2 수준에 머무르며, 일부 시제품만 Level 3 단계에 근접하는 것으로 나타났다. 국내 광산 적용 사례에서는 공정 연속성 확보, 생산성 향상, 안전성 제고, 비용 절감의 효과가 확인되었다.
- COLLAPSE
This study defines autonomous loading systems and unmanned loading equipment in mining and reviews development trends and applications by major global manufacturers. Representative unmanned loaders and excavators are compared, and their automation maturity is interpreted using the GMG Mining Automation Maturity Model. Most deployed systems rely on teleoperation supported by LiDAR, camera, and GPS sensing for real-time localization, obstacle detection and avoidance, and safety functions, with Wi-Fi based communication for control and data transmission. Current field systems are largely Level 1 to 2, while only a few prototypes approach Level 3. Korean mine cases confirm improved continuous operation, higher productivity, better safety, and reduced costs.
-
글로벌 주요 제조사의 광산용 무인 적재 장비 기술 동향 및 국내 도입 사례
-
Original Article

-
딥러닝 기반 영상 분석을 통한 건설 현장 지형 변화 검출 기법 개발
Development of the Terrain Change Detection in Construction Sites Using a Deep Learning-Based Instance Segmentation Method
-
나종호, 정유석, 오윤석, 신휴성
Jong Ho Na, Yoo Seok Jung, Yoon Seuk Oh, Hyu Soung Shin
- 본 연구는 토공 공정이 지속적으로 수행되는 대규모 건설현장에서 영상 분석을 통해 지형 변화를 감지하는 기법을 제안한다. 현장 CCTV에서 수집한 영상을 가공하여 지형 …
Footage captured by on-site CCTV was labeled to construct a terrain-object training dataset, and the data were partitioned by time to evaluate …
- 본 연구는 토공 공정이 지속적으로 수행되는 대규모 건설현장에서 영상 분석을 통해 지형 변화를 감지하는 기법을 제안한다. 현장 CCTV에서 수집한 영상을 가공하여 지형 객체 학습 데이터셋을 구축하였고, 지형 변화의 시계열성을 평가하기 위해 시점 기준으로 데이터를 분할하였다. 분할 데이터셋의 초기 2개월은 학습 데이터와 검증 데이터로 구성하였고 이후 2개월은 테스트 데이터로 분류하였다. 딥러닝 기반 인스턴스 분할 모델 기반 지형 변화 검출 실험을 수행한 결과, mAP@0.5 90.6% 수준의 정확도로 지형 객체를 안정적으로 검출하였으며, 과거 시점 영상 기반으로 미래 시점의 변화된 지형까지 감지하는 연구 결과를 확인하였다. 본 연구 결과는 영상만으로 토공 현장의 지형 변화를 인식하고 모니터링하는 가능성을 입증하였으며, 향후 장기간 시계열 예측 및 위험도 연계 알림으로 확장하여 토공 현장 안전 모니터링 솔루션의 핵심 요소기술로 활용 될 기반을 마련하였다.
- COLLAPSE
Footage captured by on-site CCTV was labeled to construct a terrain-object training dataset, and the data were partitioned by time to evaluate the time-series nature of terrain changes. Specifically, the first two months were used for training and validation, and the subsequent two months were reserved for testing. Using a deep learning–based instance segmentation model, the experiments achieved stable detection of terrain objects with an mAP@0.5 of 90.6%, and further confirmed the feasibility of detecting future terrain changes from past image frames. These results demonstrate the potential of image-only approaches to recognize and monitor terrain changes at earthwork sites and lay the groundwork for extensions to long-term time-series forecasting and risk-aware alerting, positioning the method as a core enabling technology for safety monitoring in earthwork operations.
-
딥러닝 기반 영상 분석을 통한 건설 현장 지형 변화 검출 기법 개발
-
Original Article
-
드론 및 AI 기반 타워크레인 외관 점검 및 손상 분류 체계화
Development of Drone and AI Based Framework for Exterior Inspection and Damage Classification of Tower Cranes
-
양호준, 김성도, 최요순
Hojun Yang, Seungdo Kim, Yosoon Choi
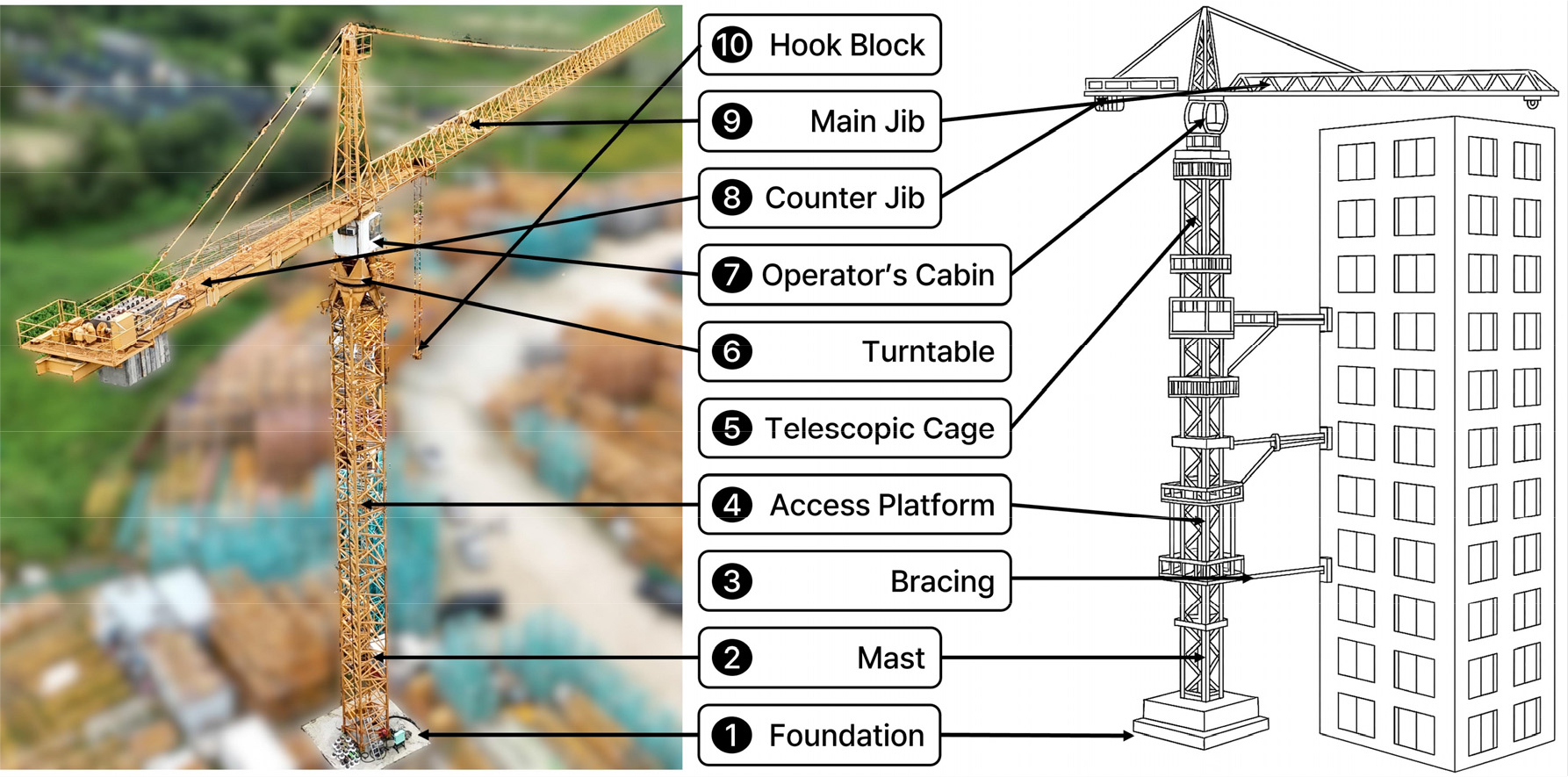
- 본 연구에서는 타워크레인의 외관검사 자동화를 위해 드론 영상과 인공지능(Artificial Intelligence, AI) 영상 분석 기술을 결합한 점검 항목 정의 체계 및 손상 유형 …
This study presents a systematic framework for defining inspection items and classifying damage types to facilitate the automation of tower crane visual …
- 본 연구에서는 타워크레인의 외관검사 자동화를 위해 드론 영상과 인공지능(Artificial Intelligence, AI) 영상 분석 기술을 결합한 점검 항목 정의 체계 및 손상 유형 분류 체계를 정립하였다. 타워크레인의 10개 주요 구성요소(기초부, 마스트, 브레싱, 안전플랫폼, 텔레스코픽 케이지, 턴테이블, 운전실, 카운터붐, 메인붐, 훅블록)를 대상으로 관련 법정 검사 기준, 기술 지침, 사고 사례를 종합적으로 분석하여 구성요소별 세부 점검 항목을 도출하였다. 또한 외관 손상 유형을 7개 대분류(균열 및 파손, 부식 및 표면 열화, 변형, 체결 불량, 와이어로프 및 시브 손상, 유압·전기 손상, 안전장치 결함)로 체계화하고, 각 유형별 정량 기준을 제시함으로써 AI 학습용 데이터셋 구축과 자동 탐지 모델 개발에 활용 가능한 표준화된 정의 체계를 마련하였다. 본 연구의 결과는 향후 스마트 점검 플랫폼 구축과 건설기계 안전진단 자동화 기술의 고도화를 위한 핵심 기초 자료로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
- COLLAPSE
This study presents a systematic framework for defining inspection items and classifying damage types to facilitate the automation of tower crane visual inspections using drone-based imaging and artificial intelligence (AI)-based image analysis. Ten major structural components of tower cranes (foundation, mast, bracing, access platform, telescopic cage, turntable, operator’s cabin, counter jib, main jib, and hook block) were analyzed by integrating legal inspection standards, technical guidelines, and accident case studies to derive detailed inspection items. In addition, seven major categories of visual damage—cracks and fractures, corrosion and surface deterioration, deformation, fastening defects, wire rope and sheave damage, hydraulic and electrical failures, and safety device defects—were systematically classified. Quantitative criteria for each category were established to standardize AI training datasets and support the development of automated damage detection models. The proposed framework provides a technical foundation for constructing smart inspection platforms and advancing automation technologies for the safety assessment of construction equipment.
-
드론 및 AI 기반 타워크레인 외관 점검 및 손상 분류 체계화
-
Original Article

-
지하 스마트팜: 현황 분석 및 지하 환경 모니터링 기반의 개념설계
Underground Smart Farms: Conceptual Design Based on Status Analysis and Environmental Monitoring
-
장수호, 강태호, 최순욱
Soo-Ho Chang, Tae-Ho Kang, Soon-Wook Choi
- 본 연구에서는 지하 유휴공간의 환경 특성을 활용하여 지하 스마트팜을 구현하기 위한 개념설계를 실시하였다. 이를 위하여 지하 스마트팜과 관련된 해외 연구동향을 분석하여, 향후 …
In this study, a conceptual design was carried out for implementing underground smart farms by utilizing the environmental characteristics of underground idle …
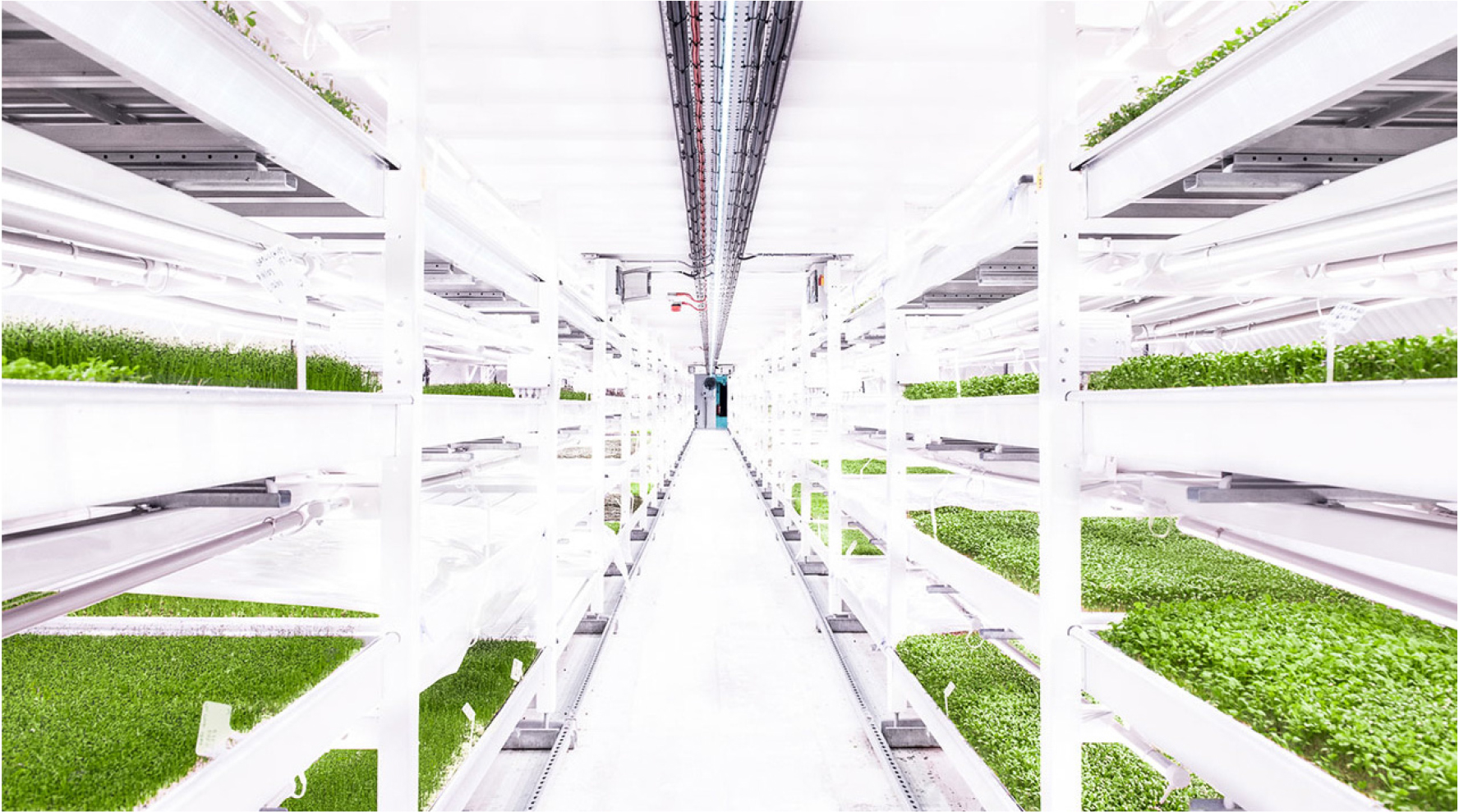
- 본 연구에서는 지하 유휴공간의 환경 특성을 활용하여 지하 스마트팜을 구현하기 위한 개념설계를 실시하였다. 이를 위하여 지하 스마트팜과 관련된 해외 연구동향을 분석하여, 향후 지하 스마트팜의 운영 최적화를 위해 필요한 모니터링 항목들을 도출하였다. 도출된 모니터링 항목들에 기반하여 지하공간 환경 특성을 모니터링하기 위한 시스템을 설계하고 제작하여 주방식 광산 내부의 유휴공간에 설치하였다. 초기 데이터들을 분석한 결과, 온도, 대기압, 이산화탄소 농도, 일산화탄소 농도 등에 있어서는 본 연구에서 고려한 세 가지 재배 방식의 운영 조건을 만족하는 것으로 나타났다. 반면, 습도와 분진에 대해서는 추가적인 대책이 필요할 것으로 판단된다. 이러한 결과를 바탕으로, 테스트 공간에 적용할 모듈형 지하 스마트팜 유닛을 설계하였다. 이때, 본 연구에서 구축한 지하 환경 모니터링 시스템과 연계하여 최적의 생육 환경을 도출하기 위한 스마트팜 모니터링 체계를 함께 제안하였다. 향후에는 본 연구에서 구축한 모니터링 시스템에 의한 장기 모니터링 결과를 바탕으로, 지하 환경에 적합한 재배 방식의 선정과 실제 지하 스마트팜 유닛의 운영을 통한 최적의 생육 환경을 도출할 계획이다.
- COLLAPSE
In this study, a conceptual design was carried out for implementing underground smart farms by utilizing the environmental characteristics of underground idle spaces. To achieve this, recent research trends on underground smart farms were analyzed to identify monitoring parameters necessary for optimizing future underground smart farm operations. Based on the identified monitoring parameters, an environmental monitoring system was designed, fabricated, and installed in the idle space of a room-and-pillar mine. Analysis of the initial data revealed that temperature, atmospheric pressure, carbon dioxide concentration, and carbon monoxide concentration satisfied the operating conditions for the three cultivation methods considered in this study. However, additional measures are deemed necessary for humidity and dust control. Based on these results, a modular underground smart farm unit was designed for application in the test space. A smart farm monitoring framework was also proposed to derive optimal growing conditions in conjunction with the underground environmental monitoring system established in this study. Future work will focus on selecting cultivation methods suitable for underground environments and deriving optimal growing conditions through the operation of actual underground smart farm units, based on long-term monitoring results from the system constructed in this study.
-
지하 스마트팜: 현황 분석 및 지하 환경 모니터링 기반의 개념설계
-
Original Article
-
Open TBM 시뮬레이터의 방향제어모델에 대한 연구
A Study on the Directional Control Model of Open TBM Simulator
-
최순욱, 강태호, 장수호
Soon-Wook Choi, Tae-Ho Kang, Soo-Ho Chang
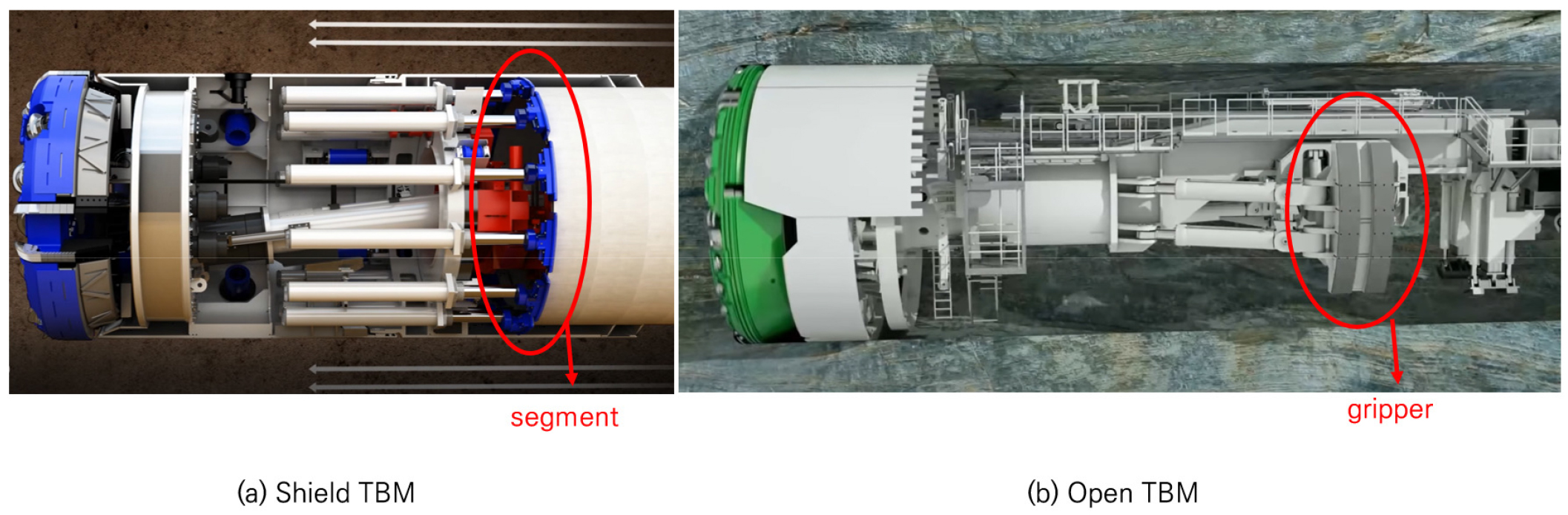
- Open TBM (Tunnel Boring Machine)공법은 양호한 암반지반에서 주로 사용하는 기계굴착장비로서 산악터널과 수로터널에 주로 적용되지만, 최근 도심지공사에서도 활용이 증대되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 Open …
The Open TBM (Tunnel Boring Machine) is a mechanical excavation equipment primarily used in sound rock formations, mainly applied to mountain tunnels …
- Open TBM (Tunnel Boring Machine)공법은 양호한 암반지반에서 주로 사용하는 기계굴착장비로서 산악터널과 수로터널에 주로 적용되지만, 최근 도심지공사에서도 활용이 증대되고 있다. 본 연구에서는 Open TBM 시뮬레이터 개발의 일환으로 메인빔 타입 Open TBM의 방향제어모델을 개발하고 시뮬레이터에 적용하는 방법을 제시하였다. Open TBM의 방향제어모델에서는 그리퍼캐리어에 설치되어 있는 실린더의 스트로크 길이를 이용하여 수평방향과 수직방향의 커터헤드 회전각을 수식화하였으며, 메인빔과 그리퍼를 연결하는 추력실린더의 전진방향 스트로크 길이를 수식화하였다. 수식화된 방향제어모델을 Open TBM 시뮬레이터에 활용하기 위해 컨트롤 패널의 제어에 따른 커터헤드의 회전과 이동에 대한 계산방법을 제시하였다.
- COLLAPSE
The Open TBM (Tunnel Boring Machine) is a mechanical excavation equipment primarily used in sound rock formations, mainly applied to mountain tunnels and waterway tunnels, but its utilization in urban construction projects has also been increasing recently. This study presents a method for developing and applying a directional control model for a main-beam type Open TBM to a simulator as part of the Open TBM simulator development. The directional control model for the Open TBM mathematically describes the horizontal and vertical rotation angles of the cutterhead using the stroke length of the cylinders installed on the gripper carrier. It also mathematically describes the forward stroke length of the thrust cylinder connecting the main beam and the gripper. To utilize the formulated directional control model in the Open TBM simulator, a calculation method for the cutterhead's rotation and movement based on control panel inputs was presented.
-
Open TBM 시뮬레이터의 방향제어모델에 대한 연구
-
Original Article
-
흑연광 지하 갱도 굴진채광 시스템 설계 및 생산 공정 시뮬레이션 모델 개발
Design of an Underground Graphite Mining System and Development of a Production Process Simulation Model
-
최요순, 정다희, 장민경
Yosoon Choi, Dahee Jung, Mingyeong Jang
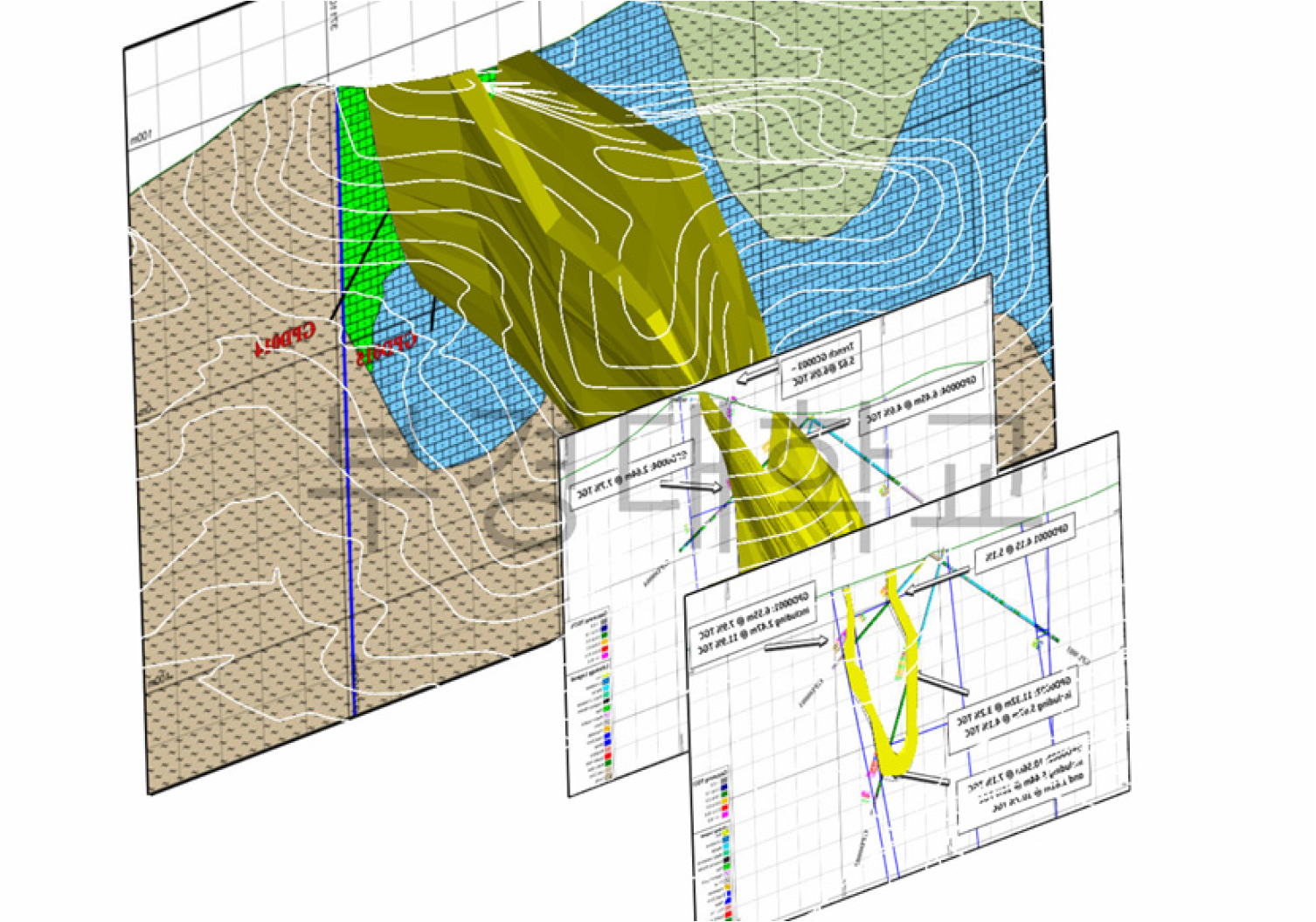
- 본 연구는 흑연광 지하채광 시스템을 설계하고, 광산 개발 공정을 평가할 수 있는 시뮬레이션 모델을 개발하였다. 제안된 모델은 3D 모델링을 통해 구축된 광체 …
This study designed an underground mining system for a graphite deposit and developed a simulation model to evaluate the mining development process. …
- 본 연구는 흑연광 지하채광 시스템을 설계하고, 광산 개발 공정을 평가할 수 있는 시뮬레이션 모델을 개발하였다. 제안된 모델은 3D 모델링을 통해 구축된 광체 정보를 활용하여 지하 운반 시스템, 지하 파쇄 시스템, 출하 시스템의 세 가지 주요 하위 시스템을 시뮬레이션할 수 있도록 구성하였다. 연구지역은 국내의 한 흑연 광체를 대상으로 하였으며, 현장 조건을 반영한 시뮬레이션 모델을 구축하였다. 개발된 모델을 적용하여 연구지역의 지하채광 시스템에 적합한 최적의 장비 운영 방안을 도출하였다. 본 연구에서 구현한 모델은 3D 모델링 기반으로 연구지역의 지하채광 시스템을 정밀하게 재현하였다. 이를 바탕으로 구축된 시뮬레이션 모델은 실제 현장에서의 운영 효율성 향상을 위해 활용될 수 있는 가능성을 보여주었다.
- COLLAPSE
This study designed an underground mining system for a graphite deposit and developed a simulation model to evaluate the mining development process. The proposed model incorporates the orebody generated through 3D modeling and simulates three major subsystems: the underground haulage system, the underground crushing system, and the shipment system. A graphite deposit in Korea was selected as the study area, and a site-specific simulation model was constructed accordingly. Using the developed model, optimal equipment operation strategies suitable for the underground mining conditions of the study area were derived. The model implemented through 3D modeling provides a comprehensive representation of the underground mining system. The results of this study demonstrate the potential contribution of the proposed simulation model to improving operational efficiency in actual field applications.
-
흑연광 지하 갱도 굴진채광 시스템 설계 및 생산 공정 시뮬레이션 모델 개발
-
Original Article
-
고준위 방사성폐기물 처분을 위한 과립형 벤토나이트의 기초 물성 특성 및 수리-역학적 거동 평가
Characterization of Fundamental Properties and Hydro-Mechanical Behavior of Granular Bentonite for High-Level Radioactive Waste Disposal
-
이종찬, 장기완, 구희권, 김석훈
Jongchan Lee, Kiwan Jang, Heekwon Ku, Sukhoon Kim
- 세계 최초로 고준위 방사성폐기물 심층처분시설(DGR)에 대한 운영허가를 획득한 핀란드에서 뒤채움재 설계가 기존의 압축 블록/펠렛 방식에서 과립형 벤토나이트로 변경됨에 따라, 과립형 재료의 기초 …
As the backfill design for the Deep Geological Repository (DGR) shifts from conventional compacted block/pellet systems to granular bentonite in Finland, the …
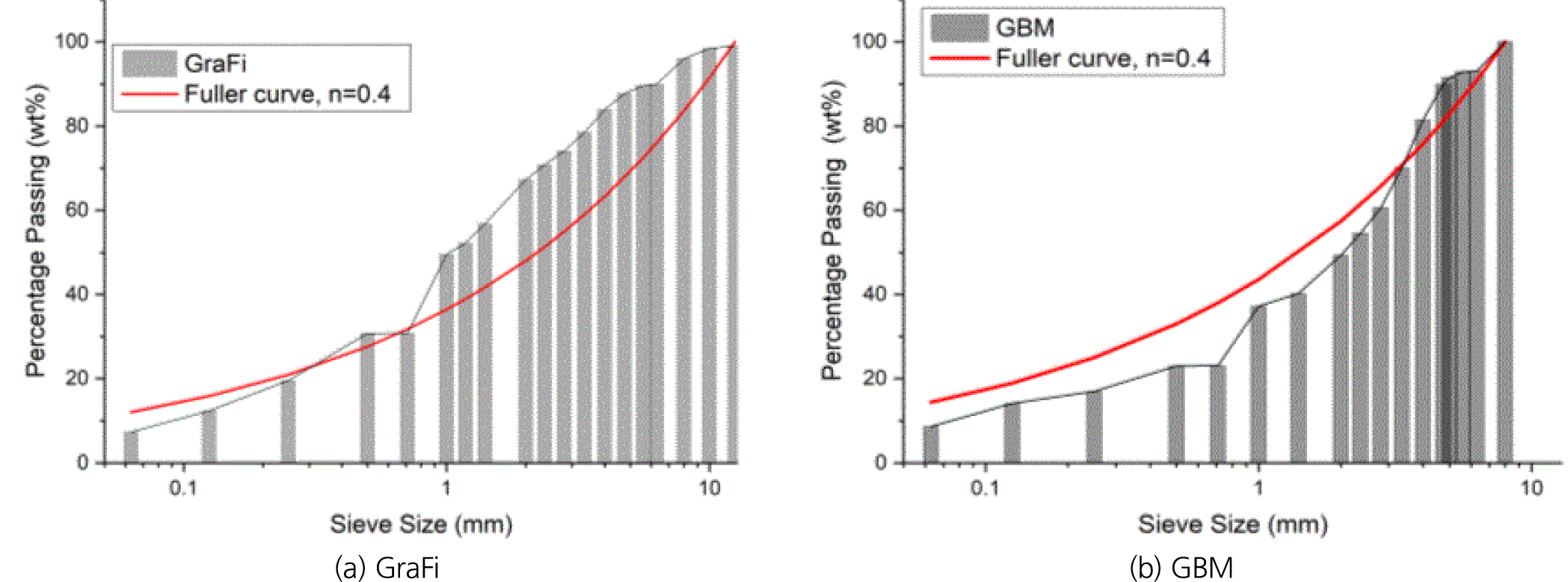
- 세계 최초로 고준위 방사성폐기물 심층처분시설(DGR)에 대한 운영허가를 획득한 핀란드에서 뒤채움재 설계가 기존의 압축 블록/펠렛 방식에서 과립형 벤토나이트로 변경됨에 따라, 과립형 재료의 기초 물성 및 장기 거동에 대한 포괄적인 데이터가 요구되고 있다. 이에 따라 본 연구에서는 각각 핀란드 및 스위스의 심층처분 프로그램에서 과립형 뒤채움재로 고려하고 있는 2가지 재료인 GraFi 및 GBM의 물리, 화학, 수리, 역학적 기초 특성을 종합적으로 비교 분석하기 위해 입도분석, 양이온교환능(CEC), 수분특성곡선(SWCC) 등 총 14개 항목에 대한 특성 평가를 수행하였다. 그 결과, 두 재료 모두 동일한 Na-벤토나이트 계열로 확인되었으나, 원광과 제조 공정에서 기인하는 뚜렷한 차이를 나타냈다. GraFi는 GBM에 비해 스멕타이트 함량, 양이온교환능 등 점토의 활성도를 나타내는 모든 지표가 상대적으로 높게 나타났으나, 제조 특성 측면에서는 GBM이 보다 높은 건조밀도로 제조되었음을 확인하였다. 또한, 1.4 g/cm3의 설치 건조밀도 조건에서 수분특성곡선의 van Genuchten 모델 파라미터를 도출하였다. 이러한 기초 물성 데이터는 향후 수리-역학적 모델의 입력 변수 및 한국형 뒤채움재 개발을 위한 핵심 기초자료로 활용될 것이다.
- COLLAPSE
As the backfill design for the Deep Geological Repository (DGR) shifts from conventional compacted block/pellet systems to granular bentonite in Finland, the world’s first country to receive an operating license for high-level radioactive waste, comprehensive data of these granular materials are required. Accordingly, this study presents a comprehensive analysis of the basic physical, chemical, hydro-mechanical properties of two materials, GraFi and GBM, which are being considered as granular backfill respectively in the Finnish and Swiss DGR programs. A total of 14 characteristic evaluations were performed, including particle size distribution, chemical composition and clay activity. The results confirmed that both materials are of the same sodium-type bentonite; however, they exhibited distinct differences originating from the source and manufacturing processes. While GraFi showed relatively higher values for all indicators representing clay activity compared to GBM, it was confirmed that GBM was produced with a higher dry density in terms of manufacturing properties. Additionally, the van Genuchten model parameters for the Soil-Water Characteristic Curve (SWCC) were derived for an installation dry density of 1.4 g/cm3. These fundamental property data will serve as input parameters for future hydro-mechanical models and as core basic data for the development of Korean granular backfill.
-
고준위 방사성폐기물 처분을 위한 과립형 벤토나이트의 기초 물성 특성 및 수리-역학적 거동 평가
-
Original Article
-
음향방출특성과 분류학습기법을 활용한 이축압축조건에서의 지하공동 손상 특성 연구
Damage Characteristics of Underground Openings Under Biaxial Compression Using Acoustic Emission and Classification Learning Methods
-
김민준, 이종원, 최준형, 김한나, 박의섭
Min-Jun Kim, Jong-Won Lee, Junhyung Choi, Hanna Kim, Eui-Seob Park
- 본 연구에서는 심부 지하공간에서의 지하공동 안정성 평가를 위해 이축압축조건하 원형 공동을 포함한 사암 시험편을 대상으로 음향방출(acoustic emission, AE) 특성과 분류학습기법을 활용한 손상단계 …
This study investigates the feasibility of predicting damage levels around underground openings under deep in-situ stress conditions by combining acoustic emission (AE) …
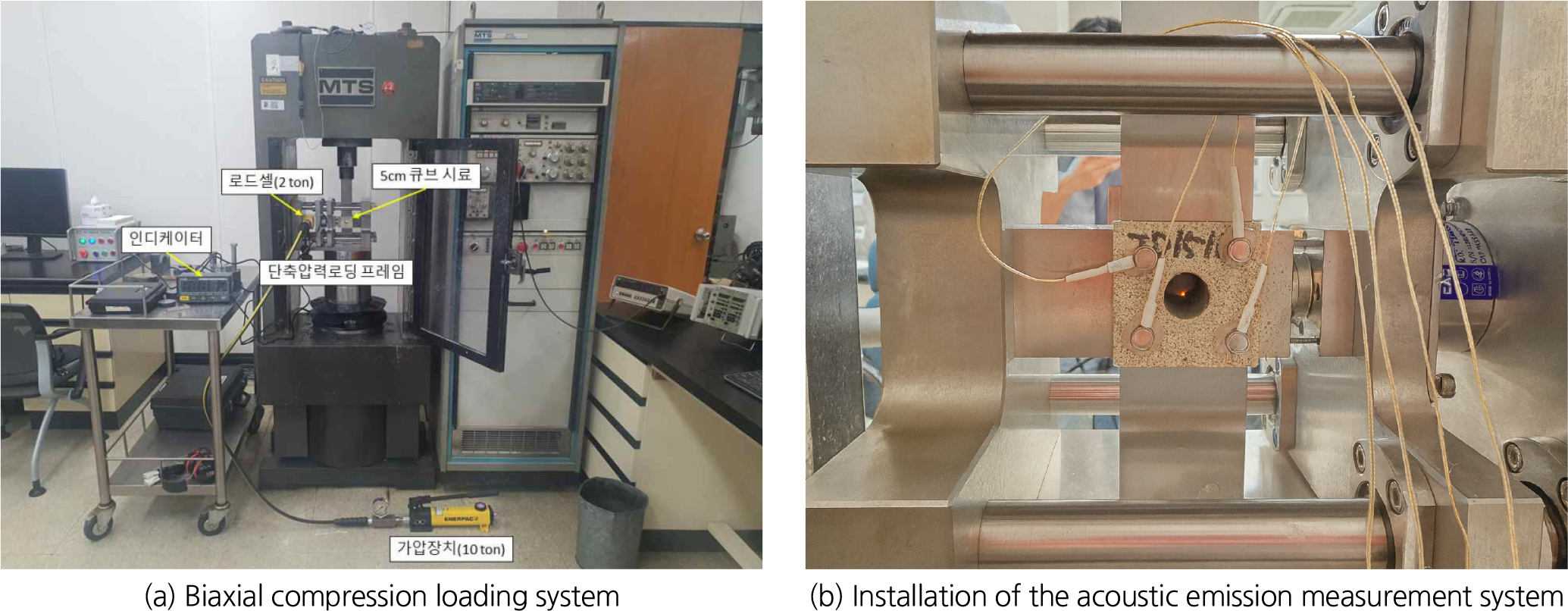
- 본 연구에서는 심부 지하공간에서의 지하공동 안정성 평가를 위해 이축압축조건하 원형 공동을 포함한 사암 시험편을 대상으로 음향방출(acoustic emission, AE) 특성과 분류학습기법을 활용한 손상단계 예측 가능성을 검토하였다. Berea 및 Idaho 사암 블록에 원형 공동을 천공한 후 두가지 횡방향 하중 조건에서 이축압축실험을 수행하였으며, 카운트(counts), 에너지(energy), 최대진폭(amplitude), 초기주파수(initiation frequency) 등 대표적인 시간 및 주파수 영역 AE 인자를 축방향 하중 이력과 연계하여 분석하였다. 그 결과, 두 사암은 약 2배의 일축압축강도 차이를 보였음에도 AE 인자들의 발생 패턴은 유사하게 나타났으며, 횡방향 하중 수준 변화에 따른 차이 또한 제한적인 것으로 확인되었다. 이는 이축압축조건에서 구속압력이 미세균열의 개방과 확장을 억제함으로써 강도 및 횡방향 하중 차이가 AE 인자에 미치는 영향을 감소시킨 결과로 해석된다. 한편, AE 인자 15개, 암반 기본물성 8개, 횡방향 하중조건 1개를 포함한 총 24개의 예측변수와 축하중 비율에 기반한 4단계 손상단계를 응답변수로 구성하여 23종의 분류학습 알고리즘을 비교한 결과, bagged trees 알고리즘이 약 93.9%의 가장 높은 예측 정확도를 보였고 각 손상단계에 대해서도 80% 이상의 분류 성능을 나타냈다. 이러한 결과는 이축압축조건에서 AE 인자와 분류학습기법을 결합할 경우 지하공동 주변의 손상단계를 정량적으로 구분할 수 있음을 보여주며, 향후 심부 지하공동 안정성 평가 및 음향방출 기반 손상 모니터링 시스템 구축을 위한 기초 자료로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 판단된다.
- COLLAPSE
This study investigates the feasibility of predicting damage levels around underground openings under deep in-situ stress conditions by combining acoustic emission (AE) analysis with classification learning methods under biaxial loading. Biaxial compression tests were conducted on Berea and Idaho sandstone block specimens containing a central circular cavity, while applying different horizontal stress levels. Representative time- and frequency-domain AE parameters, including counts, energy, amplitude, and initiation frequency, were analyzed with respect to the axial loading history. Despite an approximately twofold difference in uniaxial compressive strength between the two sandstones, the evolution patterns of AE parameters were generally similar, and the influence of horizontal stress level on AE responses was found to be limited. This behavior is interpreted as the effect of lateral confinement, which suppresses microcrack opening and propagation and thereby reduces the sensitivity of AE responses to strength and boundary stress conditions under biaxial loading. A dataset comprising 24 input features—15 AE parameters, 8 mechanical properties, and 1 horizontal stress variable—and four damage levels defined by the ratio of axial load to peak load was then constructed for classification learning. Among 23 classification algorithms tested, the bagged trees algorithm achieved the highest prediction accuracy of 93.9%, with more than 80% classification performance for each damage level. These results demonstrate that the combination of AE features and classification learning methods can quantitatively determine damage levels around circular openings under biaxial compression, and they provide a useful basis for AE-based damage assessment systems for deep underground openings.
-
음향방출특성과 분류학습기법을 활용한 이축압축조건에서의 지하공동 손상 특성 연구
-
Original Article
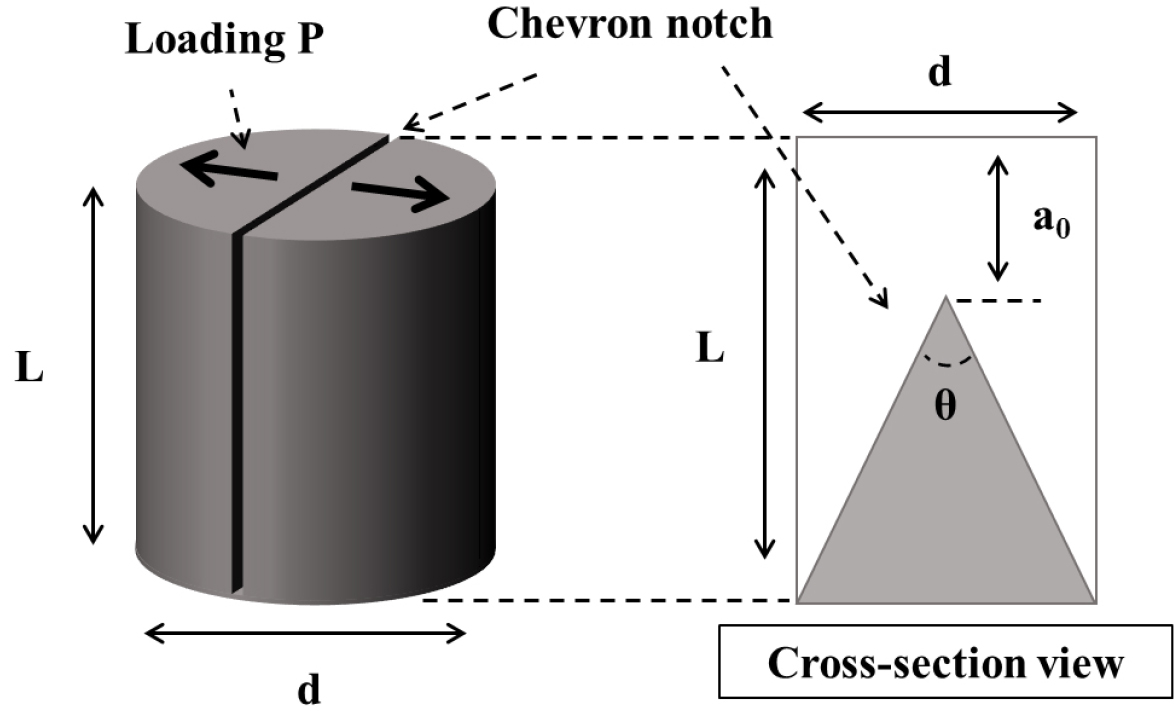
-
Short rod(SR) 방법을 이용한 화강암의 동적 Mode I 파괴인성 특성 분석
Analysis of Dynamic Mode I Fracture Toughness of Granite Using the Short Rod(SR) Method
-
김경규, 오세욱, 홍승기, 최병희, 김명선, 조상호
Gyeonggyu Kim, Sewook Oh, Seungki Hong, Byunghee Choi, Myungsun Kim, Sangho Cho
- 본 연구에서는 스플릿 홉킨슨 압력봉(SHPB) 시스템을 이용하여 영주 화강암과 황등 화강암의 동적 Mode I 파괴인성을 평가하였다. SR 방법 적용 결과, 영주 화강암의 …
This study evaluated the dynamic Mode I fracture toughness of Yeongju granite and Hwangdeung granite using a Split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) …
- 본 연구에서는 스플릿 홉킨슨 압력봉(SHPB) 시스템을 이용하여 영주 화강암과 황등 화강암의 동적 Mode I 파괴인성을 평가하였다. SR 방법 적용 결과, 영주 화강암의 파괴인성은 황등 화강암보다 약 1.08~1.16배 높게 나타났다. 두 암종 모두 하중속도 증가에 따라 파괴인성이 멱함수 형태로 증가하였으며, 회귀분석을 통해 영주 화강암의 하중속도 의존성이 황등 화강암보다 약 1.1배 큰 것으로 평가되었다. 하중조건이 정적에서 동적으로 변화함에 따라 이방성 지수는 감소하는 경향을 보였고, 이를 통해 동적 하중 조건에서는 재료 이방성이 파괴인성에 미치는 영향이 상대적으로 작음을 확인하였다. 또한, 균열개방변위 및 균열개방속도 이력곡선은 고속 카메라의 균열 전파 영상과 잘 일치하였고, 이를 통해 동적 SR 시험에서 균열 개방 및 파괴거동이 이상적으로 재현되었음을 확인하였다.
- COLLAPSE
This study evaluated the dynamic Mode I fracture toughness of Yeongju granite and Hwangdeung granite using a Split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) system. Using the Short rod (SR) method, Yeongju granite exhibited fracture toughness values approximately 1.08~1.16 times higher than those of Hwangdeung granite. For both rock types, fracture toughness increased with loading rate and followed a power-law relationship. Regression analysis further showed that the loading rate sensitivity of Yeongju granite was approximately 1.1 times greater than that of Hwangdeung granite. The anisotropy factor decreased from static to dynamic loading, indicating that material anisotropy has a relatively small influence on fracture toughness under dynamic loading. Moreover, the crack opening displacement (COD) and crack opening velocity (COV) time histories were consistent with high speed camera images of crack propagation, confirming the reproducibility of crack opening and fracture behavior in the dynamic SR test.
-
Short rod(SR) 방법을 이용한 화강암의 동적 Mode I 파괴인성 특성 분석



 Tunnel and Underground Space
Tunnel and Underground Space











